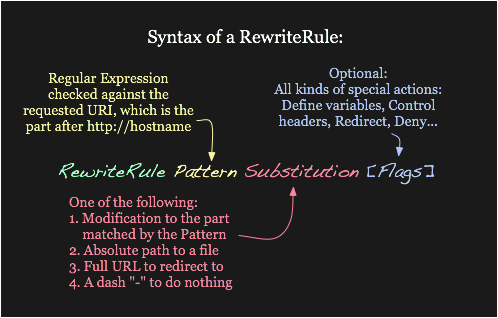
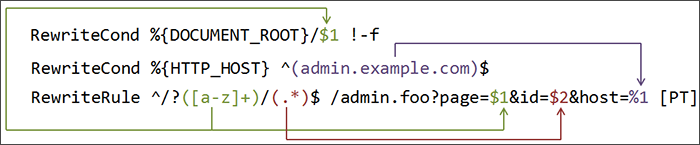
The Apache module mod_rewrite is a very powerful and sophisticated module which provides a way to do URL manipulations. With it, you can do nearly all types of URL rewriting that you may need. It is, however, somewhat complex, and may be intimidating to the beginner. There is also a tendency to treat rewrite rules as magic incantation, using them without actually understanding what they do.
This document attempts to give sufficient background so that what follows is understood, rather than just copied blindly.
Remember that many common URL-manipulation tasks don’t require the full power and complexity of mod_rewrite. For simple tasks, see mod_alias and the documentation on mapping URLs to the filesystem.
Finally, before proceeding, be sure to configure mod_rewrite’s log level to one of the trace levels using the LogLevel directive. Although this can give an overwhelming amount of information, it is indispensable in debugging problems with mod_rewrite configuration, since it will tell you exactly how each rule is processed.